| Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) Programme |
 |
Programmes > DRR >
Thematic areas of the WMO DRR Programme
Last updated: 16 August 2018
WMO thematic priorities in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) are underpinned by the Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015 (HFA), and include: risk identification, risk reduction and risk transfer.
Risk-based decision-making and disaster risk financing are critical for the development of national DRR and climate adaptation policies, institutional and financial planning, sectoral risk management and operations, for which access to meteorological, hydrological and climate services is essential.
The thematic areas of DRR Services include supporting: (1) governance and institutional frameworks at national to local levels; (2) hazard/risk analysis; (3) multi-hazard early warning systems (MHEWS); (4) sectoral risk management through improved planning, land zoning, infrastructure and urban planning, agriculture, health, transport and water resource management; (5) disaster risk financing and weather indexed financial risk transfer mechanisms; and (6) information and knowledge sharing, education and training (Figure 1). Efforts are underway to develop guidelines, standards, and training modules spanning institutional, technical and operational aspects, based on the WMO Service Delivery Strategy and consistent with Quality Management Systems (QMS) principles.
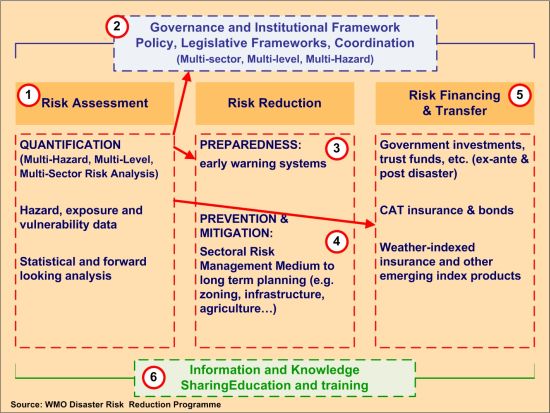
Figure 1: Elements of a comprehensive DRR Framework based on Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015
Thematic DRR User-Interface Working Groups
Four thematic DRR user-interface Expert Advisory Groups (EAGs) have been established to guide and support implementation of the DRR Work Plan and related deliverables (Figure 2). These user-interface EAGs involve leading experts from the diverse DRR user community (public and private sectors), United Nations and international partner agencies, academia as well as National Meteorological and Hydrological Services (NMHSs). These EAGs are established to: (i) guide documentation of good practices and development of user needs and requirements for products and services to support thematic areas; (ii) support development of and provide feedback on the WMO DRR knowledge products (guidelines, standards, training modules, etc); and (iii) support the implementation of the national/regional DRR projects (details of the EAGs including associated experts, deliverables and linkages to WMO Technical Commissions and Programmes can be downloaded here). The four DRR user-interface EAGs established to date, include:
-
E
xpert Advisory Group on Hazard/Risk Analysis (EAG-HRA): The EAG-HRA focuses on issues related to standards and guidelines for hazard definition, standardization of hazard databases, metadata and statistical analysis and forecasting techniques of hazard characteristics to support risk modeling. This EAG is comprised of experts from the United Nations and international development agencies with risk assessment capacities, WMO Members, private sector with expertise in risk modeling as well as experts from the WMO technical commissions. The first meeting took place in September 2012.
-
Expert Advisory on MHEWS (EAG-MHEWS): The EAG-MHEWS focuses on documentation of good practices and the development of guidelines and training modules on MHEWS. Building on the work carried out in the last four years, documentation of good practices on MHEWS WMO Guidelines on DRR and Institutional Partnerships in MHEWS are under preparation. Furthermore, WMO Guidelines on the operational aspects of MHEWS, building on the principles of QMS, are to be implemented during the 2012-2015 inter-sessional period. This EAG is comprised of leading experts from the NMHSs, disaster risk management agencies, regional agencies, international and regional development agencies and the private sector.
-
Expert Advisory Group on Climate Services for Disaster Risk Financing (EAG-CSDRF): The EAG-CSDRF was established to provide requirements for climate services for disaster risk financing in order to develop WMO guidelines for NMHS based on documentation of good practices in this area. A concrete work plan has been developed to identify, document and synthesize good practices in this area and develop relevant requirements and guidelines for climate services to support different sectors in this area. Members of the EAG-CSDRF include: internationally recognized experts from (re)insurance, sector and other financial institutions, international agencies that are facilitating these markets in the developing countries, as well as experts from academia and climate research community as well as number of NMHSs with experience in serving these markets.
-
Task Team on Meteorological, Hydrological and Climate Services for Improved Humanitarian Planning and Response: Focuses on the documentation of requirements of the international humanitarian community for meteorological and climate services and the development of products and services to support the humanitarian community’s planning and response activities at the national, regional and international levels. The Task Team includes experts from three WMO Technical Commissions including the Commission for Basic Systems (CBS), the Commission for Climatology (CCl), and the Commission for Hydrology (CHy) and eight United Nations and international humanitarian agencies.
|
|
 |
| |
